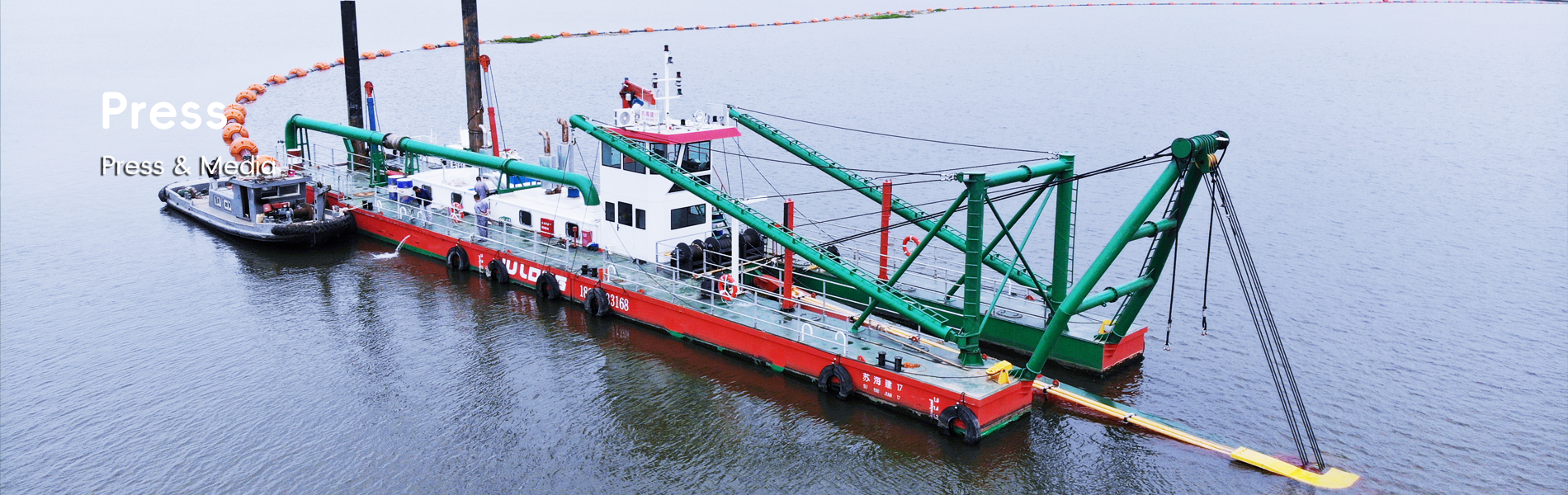
Aquatic weed harvesters are indispensable tools for quickly addressing the overgrowth of invasive aquatic plants, such as giant reed and Eurasian watermilfoil. These machines are designed to efficiently clear large areas, effectively preventing ecological disruption. Research highlights that unchecked invasive aquatic plants can diminish biodiversity and disturb local ecosystems, necessitating rapid intervention through harvesting. Moreover, removing these invasive species not only restores ecological balance but also enhances recreational activities. For instance, cleared waterways provide better access for swimming, boating, and fishing, and contribute to the restoration of natural habitats for fish and wildlife. These benefits emphasize the crucial role of aquatic weed harvesters in maintaining healthy and accessible water environments.
The process of harvesting aquatic weeds serves the dual purpose of biomass removal and nutrient extraction. By extracting nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus bound within the biomass, water quality is significantly improved. According to environmental studies, nutrient loading due to decomposing weeds can trigger harmful algal blooms, making timely removal of these plants critical. This method reduces the need for chemical treatments, aligning with sustainable aquatic management practices. By preventing nutrient accumulation, harvesters play a vital role in safeguarding aquatic ecosystems and maintaining a balanced environment for both wildlife and recreational use.
Incorporating aquatic weed harvesters into regular management strategies provides numerous long-term benefits for ecosystem maintenance. These machines support ecological balance by controlling invasive species, thereby allowing native plant communities to flourish. Studies indicate that consistent removal of invasive plants can lead to the successful restoration of natural habitats within a few growth cycles. When used in conjunction with other management practices, such as selective herbicide application, harvesters contribute to sustaining the health of aquatic systems. This integrated approach ensures a thriving, resilient ecosystem capable of supporting diverse species and recreational activities, while also reducing the environmental impact associated with chemical interventions.
Aquatic weed harvesters are designed with adjustable cutting mechanisms that allow operators to customize the depth and width, tailoring the machine's performance to specific aquatic environments. This adaptability ensures the harvester can efficiently manage diverse vegetation types, enhancing operational efficiency. According to experts, this feature is critically important as it minimizes disruptions to sediments and safeguards non-target species, further contributing to sustainable aquatic management.
Effective weed management hinges on the harvester's ability to navigate complex water bodies, such as narrow channels and densely vegetated areas. Modern aquatic weed harvesters are engineered with advanced steering capabilities to maximize maneuverability in these challenging conditions. Industry reviews consistently show that models excelling in maneuverability yield superior results, highlighting the necessity of this operational feature for efficient aquatic plant removal and waterway management.
Regular maintenance is vital to extending the life and performance of aquatic weed harvesters, ensuring they remain dependable for biomass removal. Feedback from seasoned operators suggests that machines made from durable materials require fewer repairs, significantly elevating their long-term investment value. A comparative analysis across various models reveals notable differences in maintenance needs, emphasizing the importance of selecting equipment that matches specific operational demands and maintenance capacities.
The operational efficiency of an aquatic weed harvester is largely determined by its speed and capacity, which are often influenced by the design and engine power of the machine. Industry benchmarks reveal that optimal models are capable of clearing up to 4 acres per hour under ideal conditions. Choosing a harvester with a suitable capacity is crucial for completing projects on schedule, thereby minimizing disturbance to local communities and maintaining ecological balance.
Amphibious harvesters are specifically designed for shallow water environments, making them perfect tools for managing wetlands and ponds. These machines provide excellent accessibility, enabling operators to efficiently tackle invasive plant species in areas where traditional harvesters cannot operate. A recent report from environmental agencies highlights the importance of amphibious harvesters in preserving delicate ecosystems while preventing degradation. Their unique ability to navigate shallow zones ensures minimal disruption, promoting sustainable wetland management practices.
Barge-style aquatic weed harvesters are engineered to work in deeper waters, offering robust platforms to handle large-scale biomass removal operations. These models excel in high-capacity harvesting, playing a significant role in managing nutrients within lakes and reservoirs. Notably, case studies demonstrate how these harvesters contribute to improving water quality by significantly reducing algal bloom incidences in expansive water bodies. Their sturdy design and efficiency in deep-water environments make them indispensable for comprehensive aquatic management.
Multi-functional aquatic weed harvesters bring enhanced operational flexibility by supporting various tasks besides weed harvesting, such as sediment removal and shoreline management. The growing adoption of these versatile models is driven by their cost-effectiveness and adaptability to different aquatic settings. User testimonials frequently highlight their ability to meet diverse aquatic management challenges, offering users increased value. Their multifunctionality promises significant advantages for comprehensive ecosystem maintenance, providing solutions to a wide array of environmental management needs.
Utilizing aquatic weed harvesters reduces the dependency on chemical herbicides that can adversely impact local ecosystems. By mechanically removing invasive weeds, the harmful side effects associated with these chemicals, like declining water quality in lakes, are significantly minimized. Statistics have shown that chemical treatments can lead to long-term ecological imbalances, thus advocating for mechanical harvesting as a more sustainable solution. Environmental organizations also support this method as a responsible practice to preserve ecological integrity and promote healthier aquatic environments.
Aquatic weed harvesting initiatives can be a catalyst for community-driven stewardship programs, fostering a profound sense of community responsibility. By involving local volunteers, these programs have often led to successful and lasting management of aquatic ecosystems. For instance, collaborative projects have not only achieved their environmental goals but have also enhanced community bonds. Studies demonstrate that such involvement elevates public awareness on environmental issues, encouraging more sustainable practices and long-term ecological benefits. Drawing parallels from other volunteer initiatives, these programs highlight the significant impact of community participation on natural resource preservation.
Another significant impact of aquatic weed harvesting is the sustainable compost production from the harvested biomass, which transforms waste removal into a beneficial resource for gardening and landscaping. Research indicates that composting invasive plant material not only reduces waste but also aids in restoring nutrient cycling within ecosystems, contributing to healthier soils. Communities that have embraced composting from harvested plants report enhanced local landscapes and improved environmental quality. This practice not only supports sustainability but also fosters a circular economy, where waste products are transformed into valuable resources, benefitting the wider community.