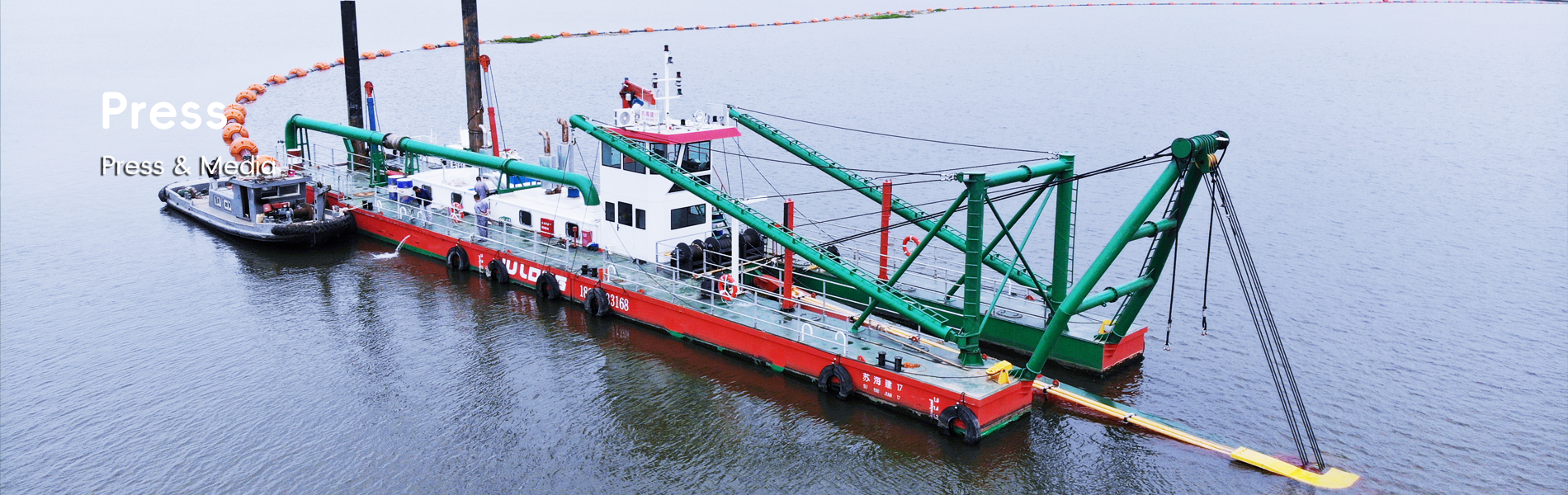
The International Maritime Organization's Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS) is crucial for ensuring the safety of dredging vessels. Established as the foremost treaty, SOLAS delivers vital safety protocols that address stability requirements, emergency preparedness, and more, specifically tailored for dredger ships. For instance, the convention includes detailed measures such as life-saving appliances, firefighting systems, and navigational safety processes, all designed to safeguard crew members and vessels in marine environments. According to IMO statistics, compliance with SOLAS has led to a marked improvement in safety outcomes in marine operations, evidenced by a reduction in accidents and incidents. These standards are integral to maintaining high levels of safety amid the varying challenges faced by dredger vessels at sea.
MARPOL Annex V plays a vital role in minimizing marine pollution by regulating waste management on dredging equipment. This annex specifically targets the reduction of dumping harmful waste from dredgers into the ocean, thereby protecting marine ecosystems. To align with these regulations, dredging operators must adopt practices such as waste segregation, meticulous record-keeping, and adhering to strict disposal methods. A study by environmental organizations shows that effective waste management has significantly reduced the negative impact on marine life and ecosystems. By following MARPOL Annex V guidelines, the dredging industry can contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable marine environment.
Adhering to standards like ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 is essential for enhancing both the quality and environmental systems within dredging operations. ISO 9001 focuses on Quality Management, ensuring operational efficiency, while ISO 14001 addresses Environmental Management, fostering a methodology that reduces the environmental footprint of a dredging project. These standards collectively boost compliance and operational effectiveness. For instance, case studies from successful dredging companies demonstrate tangible benefits, such as increased productivity and reduced environmental impact, through rigorous implementation of these standards. Adopting ISO 9001 and 14001 encourages a balanced approach to dredging, promoting sustainability along with optimal operational performance.
Understanding the EU Monitoring, Reporting, and Verification (MRV) framework is crucial for offshore dredging operations. This framework mandates that emissions from voyages involving dredging must be monitored, reported, and verified. Key metrics include greenhouse gas emissions like CO₂, CH₄, and N₂O, which are to be measured annually. Operators must develop and verify Monitoring Plans by December 31, 2024. These regulations aim to involve dredging activities in the EU Emissions Trading System (ETS).
Compliance with EU MRV has seen success in several EU member states, enhancing operational transparency and reducing environmental impact. By adhering to these regulations, dredging companies can demonstrate their commitment to sustainable practices, aligning with broader EU environmental goals.
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) plays a pivotal role in certifying gold dredge machines, ensuring these operations meet stringent safety and operational standards. The certification process is comprehensive, requiring equipment inspections, verification of safety protocols, and crew training to meet set benchmarks. Operators must prepare thorough documentation and conduct safety drills to comply with USCG standards.
Statistics reveal a positive correlation between USCG certification and reduced safety incidents in gold dredging operations. Compliance with these standards not only safeguards personnel but also enhances operational efficiency, reducing the likelihood of accidents and operational downtime.
Port State Control (PSC) inspections are essential in maintaining compliance of dredger ships within the Asia-Pacific region. These inspections focus on ensuring that dredging equipment adheres to international safety and environmental standards. Common inspection criteria include the condition of dredging equipment, crew certifications, and adherence to waste management protocols.
Recent PSC reports have highlighted issues such as outdated safety equipment and non-compliance with environmental regulations, but they also show improving compliance rates. These inspections are vital for the sustainability of Asia-Pacific maritime activities, ensuring that dredging operations remain safe and environmentally responsible.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety of dredging crews. PPE standards are essential in protecting workers from the diverse hazards encountered during dredging operations. The required PPE varies but commonly includes hard hats, safety glasses, hearing protection, gloves, and durable footwear, tailored to address specific risks like noise, heavy machinery, and water-related hazards. Statistics indicate a significant reduction in workplace injuries in dredging after rigorous implementation of PPE standards. For instance, after strict adherence to PPE protocols, many companies reported decreases in injury rates by up to 30% over five years. This underscores the necessity of adhering to PPE standards to maintain safety on the dredging field.
The International Safety Management (ISM) Code is vital for dredger ship management and plays a pivotal role in crew training. This code establishes safety management practices aboard ships to ensure safety at sea, prevent human injury or loss of life, and avoid damage to the environment, particularly the marine ecosystem. Under the ISM Code, key management responsibilities include fostering a safety culture, conducting risk assessments, and establishing emergency procedures. Evidence supports the code's efficacy, showing marked improvements in safety. Ships following ISM guidelines have reported fewer accidents and incidents, underscoring the code's impact on enhancing overall maritime safety.
Emergency response training is mandatory for dredging crews, ensuring they are prepared to handle potential crises. This training encompasses a wide range of scenarios, such as fire outbreaks, collision avoidance, and man-overboard situations. Emphasis during these sessions is placed on real-life applications through drills and simulations. Notably, effective emergency training has been linked to reduced risks during actual operations. For instance, a well-trained crew aboard a dredger in 2021 was able to effectively manage a sudden machinery failure without incident, highlighting the life-saving value of thorough emergency preparedness programs.
The Ballast Water Management Convention plays a crucial role in safeguarding marine ecosystems by preventing the transfer of invasive species via dredging ships. This convention mandates stringent measures for treating, monitoring, and reporting ballast water discharges to limit the unintended spread of non-native aquatic organisms. Dredgers must comply with regulations by implementing systems that effectively treat ballast water to meet international standards. One significant outcome of adherence to these standards is the significant reduction in ecological disturbances due to invasive species. According to the International Maritime Organization (IMO), effective ballast water management has led to improved biodiversity in affected areas, highlighting the environmental benefits of these compliance measures.
Underwater noise from dredging activities poses a significant threat to marine life, disrupting communication, navigation, and even the survival of various species. To mitigate these effects, dredging operations are adopting innovative strategies such as utilizing quieter dredging equipment and modifying operational procedures to minimize noise pollution. Techniques like bubble curtains and noise baffles are also implemented to reduce acoustic disturbances. Research has demonstrated that these noise mitigation measures have positive effects on marine ecosystems, as observed in studies where improved behavioral responses and recovery in affected marine populations were reported post-implementation.
Routine sediment contamination testing is vital for maintaining environmental compliance and protecting marine habitats during dredging operations. These tests assess the presence of hazardous substances, such as heavy metals and organic pollutants, in sediments that are potentially disturbed by dredging. To ensure compliance, dredging operations must adhere to specific testing protocols, including sampling, laboratory analysis, and monitoring of contaminant levels. Numerous studies underscore the adverse effects of sediment contamination on marine ecosystems, which can lead to the degradation of habitats and declines in marine species. Therefore, implementing rigorous testing procedures is essential to prevent environmental harm and ensure the sustainability of marine ecosystems.
Annual surveys are essential for ensuring the integrity of dredging equipment and complying with industrial standards. These surveys require a meticulous examination of various components, such as the hull, machinery, and safety systems, to detect any wear or damage that could impede operation. If these issues are identified early, they can be addressed before leading to more significant failures. Non-compliance can result in suspension of operations and penalties, affecting the overall reputation of the company. An example in the industry is when a dredging company discovered severe corrosion during an annual inspection, preventing a potential mechanical failure that could have led to severe downtime and financial loss.
Digital recordkeeping has transformed the way compliance audits are conducted in the dredging industry. By digitizing their record management, companies can streamline the audit process, ensuring that all documentation is accurate, up-to-date, and easily accessible. Digital tools like compliance management software enable efficient tracking of certification standards and simplify data analysis. This shift towards digital records not only saves time but also increases the accuracy of compliance data. As evidence, companies that have adopted digital recordkeeping have reported a 30% improvement in their compliance rates, illustrating the benefits of using technology for efficient audit preparation and execution.
The classification rules for dredger ships are often updated to incorporate new safety standards, technological advancements, and environmental regulations. These updates are critical as they directly affect certification and operational practices. The process involves consultation with key stakeholders, including shipowners, regulatory bodies, and technical experts, to ensure comprehensive consideration of all maritime industry changes. A notable change in recent years was the introduction of stricter emissions standards, significantly impacting operational procedures as dredger ships now require advanced filtration systems. Understanding and adapting to these updates is crucial for maintaining compliance and operational efficiency.