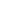
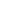
Understanding and calculating the critical velocity in hydraulic systems is crucial for optimizing dredging operations. It is defined as the minimum speed needed to keep sediment suspended, preventing the pipeline from clogging. The formula to calculate critical velocity considers the specific gravity of the slurry, flow rates, and pipeline diameter. For instance, in a case study by J.F. Brennan Company, accurate calculations of critical velocity improved dredger productivity significantly by preventing downtime due to pipeline blockages. This emphasizes the importance of these calculations in achieving efficient dredging operations.
To ensure efficient dredging, it is vital to balance sediment concentration with flow rates. Imbalances can lead to inefficiencies, such as sediment settling or unnecessary wear on equipment. Monitoring and adjusting sediment concentration are essential practices to maintain optimal flow rates. Research highlights the consequences of poor sediment management, including reduced operational efficiency and increased maintenance costs. Effective sediment management methods ensure consistent slurry transportation, maximizing productivity in dredging operations.
The diameter of the discharge pipeline plays a pivotal role in slurry transport efficiency. A smaller pipeline diameter requires higher velocity to move the slurry, while a larger diameter can allow slower velocities. Best practices involve selecting the appropriate pipeline diameter for specific dredging operations to minimize energy loss and increase efficiency. Industry guidelines suggest using research findings to determine proper pipeline sizing, ensuring slurry is effectively transported without unnecessary energy expenditure. These considerations are crucial for optimizing the flow and transport of materials in dredging projects.
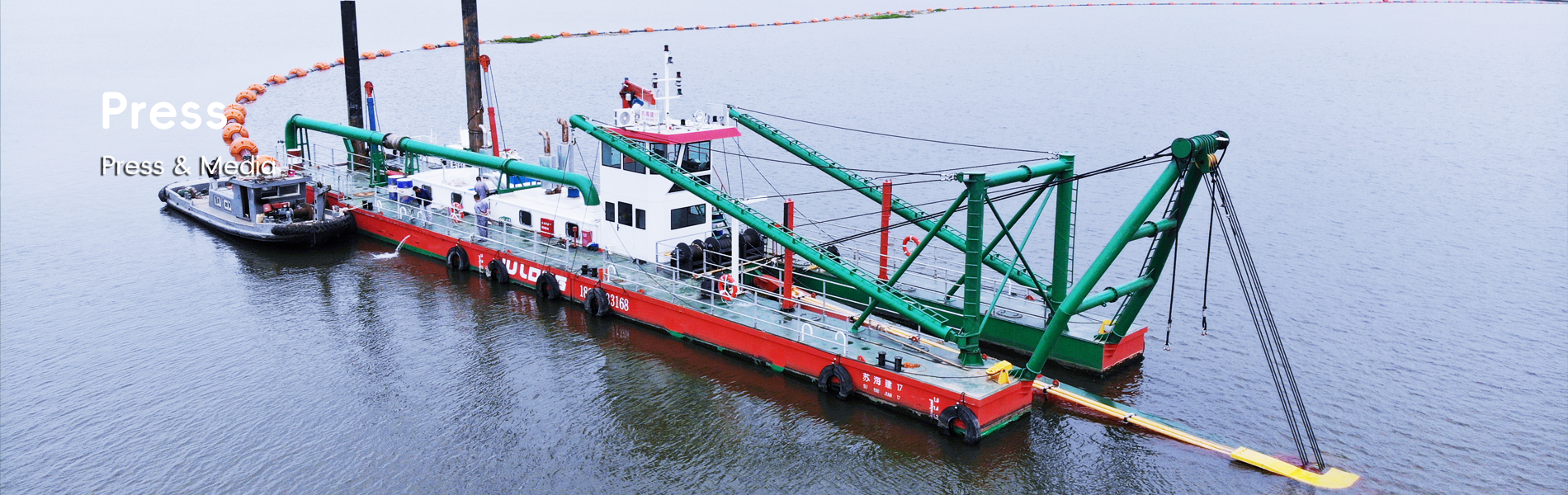
The mechanics of dredger cutter suction systems play a crucial role in enhancing dredge efficiency. These systems operate by applying a rotating cutter head to dislodge material on the sea or riverbed, which is then suctioned through a pipeline to be deposited at a designated location. This technology has been pivotal in boosting dredger productivity, with some statistics indicating up to a 30% increase in operational efficiency. As the industry continues to advance, experts forecast ongoing innovations in cutter suction systems, suggesting that the future of dredging equipment will see enhanced precision and reduced environmental impact.
GPS and DGPS technologies are instrumental in enhancing the precision of dredging activities, leading to more accurate and efficient outcomes. These technologies allow for precise navigation and positioning, ensuring that dredging operations can target specific areas with minimal error. DGPS offers even greater accuracy over traditional GPS, with differential corrections providing improved positional data. Recent marine projects have demonstrated substantial improvements in operational efficiency through the use of these technologies, highlighting their critical role in modern dredging operations.
3D visualization tools have become increasingly prevalent in marine construction and dredging projects. These tools enable stakeholders to create detailed visual simulations that improve project planning, risk assessment, and engagement. The ability to visualize complex scenarios and outcomes aids in minimizing uncertainties and optimizing resource allocation. When integrated into dredging operations, 3D visualization has shown measurable increases in project efficiency, with examples highlighting enhanced collaboration and decision-making among project teams.
When it comes to dredging operations, selecting the right pump system—centrifugal or hydraulic—is crucial for maximizing efficiency. Centrifugal pumps are commonly used for moving water and slurry due to their ability to handle large volumes effortlessly. On the other hand, hydraulic pumps offer superior control and efficiency in transferring denser materials, making them suitable for specialized dredging tasks. In terms of efficiency metrics, centrifugal pumps generally perform better in low-density conditions, while hydraulic pumps excel in high-density scenarios. Research consistently supports these trends, highlighting that each pump type has its optimal application depending on the dredging context.
In dredging projects, effective dewatering techniques play a pivotal role in sediment management, allowing for improved productivity and compliance with environmental regulations. Methods such as geotextile dewatering tubes and mechanical presses are standard practices that significantly reduce water content in dredged material. By decreasing the volume of material needing disposal, these techniques not only enhance dredger productivity but also lower overall disposal costs. Recent statistics suggest advanced dewatering methods can result in a 30-50% reduction in costs and project time, underscoring their value in modern dredging operations.
Jet pump systems are designed to prevent clogging within dredging pipelines, thus ensuring continuous and efficient operation. These systems use high-pressure jets to break up sediments and keep them suspended, preventing them from settling and obstructing the pipeline. Implementing best practices such as regular maintenance checks and monitoring flow rates can further optimize their efficacy. Successful cases, like those from large-scale dredging initiatives, show that jet pump systems can improve overall productivity by up to 40%, demonstrating their effectiveness in maintaining uninterrupted dredger operations.
Specialized training programs are vital for dredger ship operators to ensure both safety and operational efficiency in marine projects. Certification requirements, such as those from recognized maritime bodies, alongside continuous education, play a crucial role in honing operator skills. This consistent upskilling not only fortifies safety standards but also boosts overall dredger productivity. For instance, companies that have invested in robust training programs have reported significant increases in productivity, demonstrating the direct benefits of well-trained operators. A focus on continuous learning and adherence to certification criteria is key to optimizing dredging operations.
Implementing adaptive strategies is essential when encountering variable site conditions during dredging projects. These strategies enhance the efficiency of operations, allowing for a flexible approach that accommodates different environmental scenarios. For example, operations in areas with fluctuating tides or variable substrates have seen marked improvements when adaptive methods are employed. Research indicates that flexible project management significantly boosts productivity, showcasing the importance of adaptive strategies in surmounting site-specific challenges. By tailoring approaches to site-specific conditions, dredging projects can maintain high levels of effectiveness and efficiency.
Monitoring systems play a critical role in optimizing the performance of aquatic weed harvesters. By integrating advanced technology into these systems, operators can achieve greater efficiency and effectiveness. Technologies like real-time data collection and remote sensing allow for precise tracking and adjustments, boosting operational productivity. Successful implementations of these monitoring systems have been documented, exhibiting notable improvements in the management of aquatic weed harvesting activities. These technological advancements facilitate better decision-making and operational adjustments, enhancing the overall productivity of harvesting processes.