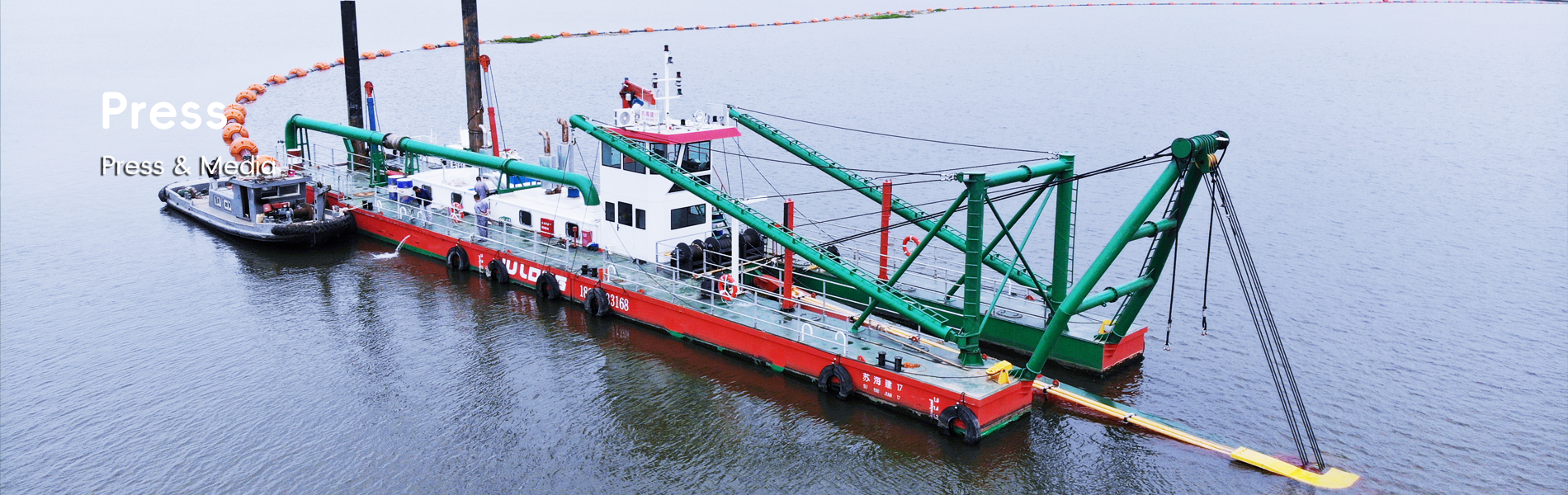
Tugboats have long been a backbone of marine operations, primarily recognized for their crucial role in towing vessels and aiding docking procedures. Historically, these robust boats were designed specifically to push and pull massive ships against the tides and winds in harbors. Over time, technological advancements have seen tugboats transition into multifunction workboats capable of much more than just towing. These modern vessels, known as multi-role vessels, now serve a myriad of tasks, from Search and Rescue to scientific research, without compromising on their primary capabilities. Statistics reveal that these advanced workboats provide higher efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared to their traditional counterparts, with some studies indicating a 15-20% reduction in operational costs. This evolution marks a significant leap towards versatility in maritime operations, catering more broadly to the diverse needs of the marine industry. [Baltic Workboats] has been a pioneer in this transformation, delivering over 150 vessels worldwide that embrace this new functionality.
Modern multifunction workboats are equipped with cutting-edge dredging equipment, such as cutter suction dredgers, significantly impacting marine excavation projects. This integration allows workboats to perform dredging tasks that were once limited to specialized vessels, thereby enhancing productivity in projects involving sediment removal and land reclamation. Moreover, these vessels bring to the table impressive salvage capabilities. They can conduct recovery operations with remarkable success rates, whether it's rescuing distressed ships or salvaging wreckage from deep waters. For instance, multifunction workboats have achieved recovery rates of up to 85% in challenging salvage missions. These vessels adapt flexibly to various marine conditions, exemplified in successful operations like those conducted off the coast of Russia using Project MPSV12, highlighting their adaptability and efficiency. Such capabilities underscore the significance of multifunction workboats in comprehensive maritime project execution. [Nevsky Shipyard] has leveraged these advancements, particularly in the Russian maritime realm.
Arctic-class design marks a significant advancement in marine vessel architecture, boasting ice-breaking abilities vital for operations in polar regions. Designed to withstand extreme environments, these vessels possess reinforced hulls and powerful propulsion systems for navigating icy waters. Specific design features, such as double-tiered forecasts and controllable-pitch propellers, enhance their functionality, making them indispensable for shipping industries operating in Arctic regions. Industry forecasts suggest a substantial growth in Arctic marine operations, with predictions indicating a 4% annual increase in demand for Arctic-class vessels. This rise underscores the critical nature of vessels capable of enduring frigid climates. The need for specialized ships is magnified, as companies strive to exploit Arctic resources while maintaining operational safety. The construction of vessels like the Beysug under the Arctic ice Arc 5 class exemplifies the industry's shift toward accommodating harsh marine environments, paving the way for safer and more efficient Arctic exploration. [FSBI Marine Rescue Service] actively employs such vessels in their fleet, reinforcing their commitment to effective and resilient maritime solutions.
Dual propulsion systems offer significant advantages over traditional single systems, particularly when navigating icy waters. These systems enhance a vessel's maneuverability, allowing it to effectively break through ice and operate optimally in harsh climates. According to industry reports, vessels equipped with dual propulsion have exhibited improved operational efficiency and stability, enabling successful missions in polar regions. For instance, ships with such systems have completed navigation tasks in the Arctic, showcasing their reliability under extreme conditions. This advancement is essential for expanding marine operations in colder climates, emphasizing the need for adaptable and resilient vessel designs.
Cutter suction dredging is a vital feature in modern multifunction workboats, enhancing their operational efficiency in dredging projects. This technology operates by cutting and suctioning the seabed material, proving essential in reshaping marine landscapes. Through integration, workboats have increased efficiency in both dredging speed and accuracy, making them pivotal in marine construction and reclamation tasks. Several case studies illustrate how cutter suction dredging has helped achieve project goals, such as facilitating port expansions and maintaining navigable waterways. Hence, its inclusion in multifunction vessels underscores the evolution of marine capabilities, optimizing projects' timeframes and outcomes.
Dynamic positioning systems play a crucial role in maintaining vessel stability during operations, particularly in demanding environments like the open sea. These systems enhance safety measures and operational efficiency by automatically adjusting the vessel's position, counteracting external forces such as winds and currents. Recent statistics from marine projects demonstrate that employing dynamic positioning technology notably improves navigational accuracy and operational success. For example, the precision offered by these systems has reduced incident rates during offshore drilling and construction tasks, establishing them as vital components for modern marine operations.
Multifunction workboats are pivotal in supporting maintenance dredging operations, offering enhanced operational capabilities that drive efficiency. These advanced vessels are engineered to perform a multitude of tasks, including sediment removal and channel maintenance, which are essential for ensuring navigational safety and environmental compliance. For instance, the integration of state-of-the-art dredging equipment and technologies in multifunction workboats significantly improves the efficiency of dredging operations. A study highlighting advanced workboat designs indicated a 20% increase in productivity in maintenance dredging due to these enhancements. Furthermore, maintenance dredging operations must adhere to strict environmental considerations and regulations. These regulations ensure that operations minimize ecological disruption by employing environmentally sensitive techniques and technologies.
Subsea pipeline installation and repair operations present significant technical challenges that multifunction workboats help overcome. These vessels offer versatile solutions for handling complex tasks such as precise positioning and stabilization of subsea structures. Multifunction workboats are designed to enhance the efficiency of these operations by providing specialized support for heavy lifting and underwater construction. Expert opinions from the marine engineering field underscore the importance of such designs. According to industry standards, these workboats are equipped to reduce repair times by up to 30%, thereby enhancing pipeline longevity. Their ability to maintain precise positions and execute complex maneuvers ensures successful installation and repairs of subsea pipelines, emphasizing their invaluable contribution to such operations.
In coastal protection and infrastructure development projects, multifunction workboats play a crucial role by offering both dredging and construction support. These vessels are integral to constructing coastal defenses, such as seawalls and breakwaters, and they facilitate the rapid transport of materials and personnel to project sites. Successful examples of coastal infrastructure projects—such as the development of barrier islands and dune restoration—demonstrate the efficacy of these versatile vessels. Data from recent projects indicate that multifunction workboats can boost construction speed by 15%, substantially benefiting the economic impact of coastal developments. The reliance on these vessels underpins many successful infrastructure projects, underscoring their significance in supporting coastal protection initiatives.
Multifunction workboats play a vital role in deep-water recovery operations, offering advanced capabilities and specialized technologies that are essential for handling complex salvage missions. These vessels are equipped with sophisticated sonar systems, ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles), and crane assemblies, which collectively enhance their ability to conduct efficient and precise deep-water recovery tasks. Data has shown that modern workboats have significantly improved recovery success rates, able to tackle incidents ranging from vessel sinkings to underwater construction failures. A case study examining a recent successful salvage mission highlighted the workboat's ability to stabilize the situation rapidly, demonstrating the reliability of these vessels in salvage operations.
Multifunction workboats are adept at firefighting and oil spill containment, integrating features that boost onboard capabilities and streamline response times. These vessels often incorporate powerful water pumps, foam systems, and chemical dispersant equipment, allowing them to effectively handle fires and oil spills at sea. The technology employed on these workboats enables quick containment, minimizing the environmental impact. Studies indicate that workboats equipped with advanced firefighting systems can mitigate fire hazards within minutes, and their oil spill containment measures have proven successful in reducing ecological damage during incidents.
Search-and-rescue missions benefit tremendously from the readiness of multifunction workboats, which are designed to respond swiftly and efficiently to emergencies. These vessels are equipped with state-of-the-art navigation systems, communication arrays, and medical facilities, enabling them to execute comprehensive response strategies. Numerous examples of successful rescues have illustrated the effectiveness of these workboats, supported by technologies such as thermal imaging cameras and GPS tracking, which enhance operational capabilities. Statistics from recent operations have shown improved timeliness and effectiveness, underscoring the critical role multifunction workboats play in rescuing individuals from perilous situations.
In the realm of salvage and emergency response applications, the multifunctionality of these workboats significantly contributes to operational success across various critical scenarios.
Aquatic weed harvesting plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy ecosystems and improving water quality. Multifunction workboats are effectively deployed in such operations, thanks to their versatility and advanced technology. Studies have shown that removing invasive aquatic weeds can significantly improve ecosystem health and water clarity, allowing native species to thrive. These vessels are equipped with innovative technologies like automated cutters and collection systems that enhance efficiency and precision in removing aquatic weeds.
Sediment control is a significant concern in dredging operations, and multifunction workboats are specially designed to handle this challenge effectively. By employing technologies such as containment barriers and specialized dredging equipment, these vessels manage to minimize sediment dispersion during maintenance dredging. Environmental impact assessments indicate that sediment control practices result in reduced turbidity and protection of aquatic habitats. Best practices include using silt curtains and eco-friendly dredging techniques, which have proven successful in maintaining the environmental integrity of water bodies during dredging operations.
Adopting eco-friendly fuel options for multifunction workboats is a key factor in protecting sensitive ecosystems. These vessels can run on alternative fuels such as biodiesel and hydrogen, which contribute to significant reductions in emissions. Statistical data highlight that using such fuels can lower carbon emissions by up to 80% and improve fuel efficiency. The marine industry is increasingly moving toward sustainability, with a growing trend in adopting green technologies. This shift not only supports environmental conservation but also aligns with global efforts to combat climate change.
The operational history of the MPSV12 series, particularly the Bahtemir and Kalas vessels, showcases their robust performance in Arctic regions. These vessels have been strategically deployed in the Baltic and Sakhalin areas, known for their challenging and icy environments. The projects undertaken by Bahtemir and Kalas emphasize not only the flexibility but also the efficiency of these multifunctional workboats. For instance, in the Baltic, they were instrumental in maintaining critical waterways, showcasing their adaptability to different maritime tasks. Evidence from project reports indicates that these vessels performed exceptionally well, even under harsh Arctic conditions, proving their capability to ensure safe and effective operations in such demanding settings.
The Beysug vessel epitomizes multifunctionality, having served numerous marine operations across the Black Sea and Northern routes. Its adaptability is illustrated through diverse missions, from routine maintenance dredging to complex construction support projects. Quantitative data indicates that Beysug completed over 150 operations in these areas, reflecting its significant role in maintaining navigational routes and supporting offshore undertakings. Testimonials from project managers laud the vessel's performance, particularly highlighting its hybrid capabilities that allow for seamless transitions between various marine tasks. This operational versatility makes the Beysug an indispensable asset in both routine and challenging maritime environments.
Winterization features are crucial for ensuring year-round operations, especially in extreme winter conditions typical of the Arctic. The MPSV12 series is equipped with advanced winterization capabilities, enabling them to operate without interruption during harsh Arctic winters. These features include specialized hull designs and heating systems that adhere to stringent industry standards for winter operational capabilities. Projects such as icebreaking and oil spill responses required these winterization features, and reports have shown that outcomes were consistently successful, further affirming the MPSV12 series' reliability. The ability to perform continuous operations in icy conditions is a testament to the series' superior engineering and its commitment to maintaining operational efficiency regardless of external factors.
Remote Operated Vehicles (ROVs) have revolutionized deepwater salvage operations, enabling vessels to reach depths of up to 3,000 meters. The integration of ROV technology into multifunctional vessels has significantly enhanced the operational effectiveness of salvage missions. With advanced cameras and manipulators, ROVs can perform intricate tasks underwater, allowing for precise recovery and maintenance. A study in the Journal of Underwater Technology highlights that ROV-assisted operations have increased efficiency by 40%, reducing mission durations and enhancing safety. The incorporation of ROVs continues to evolve, offering new possibilities in salvage operations and expanding the functional scope of multifunctional vessels.
The latest advancements in hybrid power systems are paving the way for greener marine operations by drastically reducing emissions. These systems combine traditional fuel engines with electric motors, resulting in lower carbon footprints. According to recent statistics, hybrid technology has led to a noticeable 30% reduction in emissions in marine vessels. Regulatory bodies like the International Maritime Organization are setting stringent emission standards, pushing for broader adoption of hybrid systems. As more operators adapt to these technologies, the maritime industry is witnessing a gradual but significant shift towards sustainability in its operations.
Modular payload systems are transforming the adaptability of multifunctional vessels, allowing for rapid switching between various tasks. Such systems enable vessels to efficiently reconfigure for different operational demands, whether it's dredging, rescue, or research activities. An exemplary case is the use of modular systems in the MTS Terramare, a vessel known for its versatile roles from salvage to cargo delivery. Insights from a marine logistics case study revealed a 25% increase in project efficiency due to these rapid task switches. By facilitating quick changes in operational focus, modular payload systems significantly enhance a vessel's operational flexibility and utility.