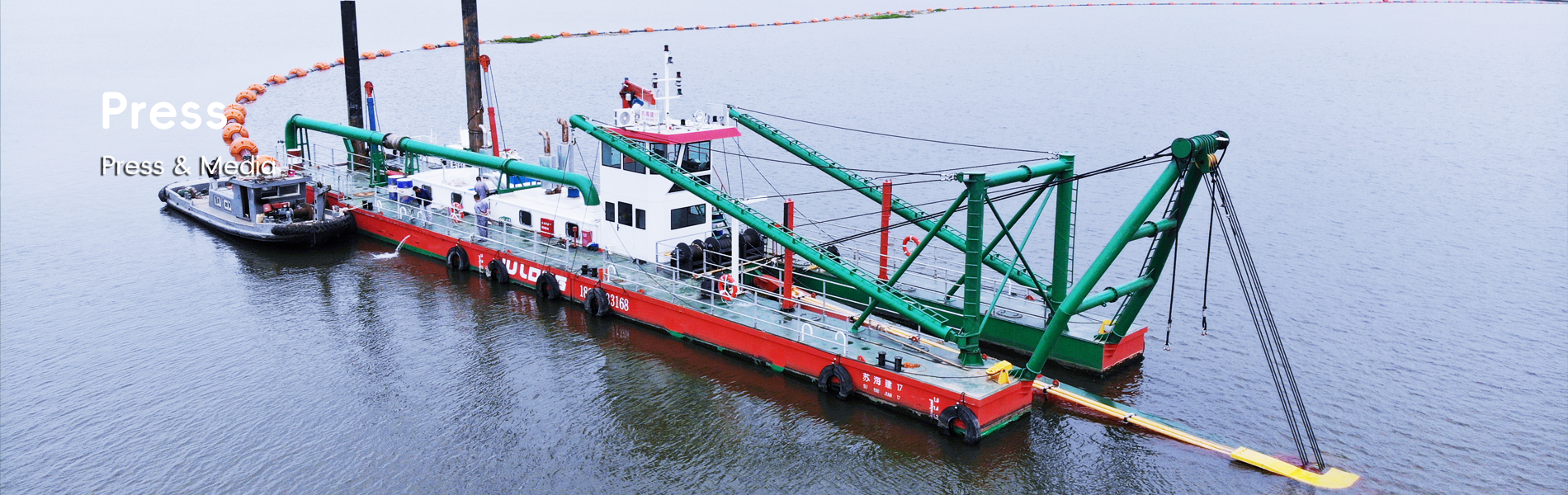
Dredging equipment plays a crucial role in managing sediment buildup in lakes and rivers. These machines are designed to remove accumulated sediments from the bottom and banks of water bodies, effectively restoring depth and improving water quality. Various types of dredgers, including hydraulic and mechanical dredges, offer specific functionalities catering to different needs. For example, hydraulic dredgers use suction to displace sediment, making them ideal for fine-grain sediment removal, while mechanical dredgers are better suited for rocks or large debris. Research indicates that sediment buildup can reduce oxygen levels, impacting aquatic life and boat navigation, underscoring the importance of regular maintenance. In case studies, such as the dredging of the Cuyahoga River, sediment removal has significantly improved aquatic habitats, boosting both biodiversity and water clarity.
Aquatic weed harvesters are essential tools for maintaining ecological balance by managing excessive aquatic plant growth. These machines are akin to oversized lawn mowers designed for water bodies, cutting and collecting weeds and other unwanted vegetation. Compared to manual methods, different models of aquatic weed harvesters vary in efficiency and environmental impact. Some are more suited for shallow waters, while others are designed for deeper lakes. Recent studies highlight the surge in aquatic weed growth due to nutrient pollution, which disrupts local ecosystems. Effective weed management, using harvesters as part of a broader strategy that includes monitoring water quality and controlling nutrient input, can significantly restore ecological stability.
Amphibious and floating excavators offer highly versatile solutions for complex water management tasks. These machines are uniquely equipped to operate in both terrestrial and aquatic environments, making them ideal for projects like land reclamation and habitat restoration. Their applications extend beyond standard maintenance, addressing issues from wetland construction to canal dredging. Market research reveals a growing demand for such versatile equipment, driven by increasing environmental awareness and land-use pressures. Notably, a case study involving a floating excavator in the Netherlands showcased its effectiveness in restoring natural watercourses, which had been previously obstructed by sediment and vegetation.
Aeration systems dramatically enhance water quality by increasing oxygen levels, which are vital for the survival of aquatic life. By breaking the water's surface, these systems allow air to infuse into the waterbody, combating issues like stratification and thermocline. Various types of aerators exist, including diffused and surface aerators, each with distinct impacts on water environments. Research has shown a strong correlation between aeration and improved biodiversity in lakes and rivers, as oxygenated water supports a wider variety of life. When installing an aeration system, consider factors such as the size of the water body and the specific oxygen demands to maximize ecological benefits.
Lake maintenance presents a unique set of challenges, primarily due to their still nature, which leads to sediment accumulation and vegetation overgrowth. Using specialized tools like dredging equipment and aquatic weed harvesters can effectively address these challenges. Dredgers are adept at managing sediment buildup, enhancing water depth, and promoting healthier ecosystems. Meanwhile, aquatic weed harvesters help control excessive vegetation, maintaining a balance in the aquatic ecosystem. Choosing the best tools for lakes largely depends on environmental factors such as depth and size. For example, shallower lakes might benefit more from regular dredging, while larger lakes with more pronounced vegetation growth could utilize high-capacity weed harvesters. Successful lake management projects often illustrate the impact of using these tools, highlighting improved water quality and ecosystem health.
Maintaining rivers involves addressing the dynamic flow and controlling erosion, tasks that demand specific tools like dredgers and bank stabilization equipment. Unlike lakes, rivers have continuous flow dynamics that exacerbate sediment displacement and erosion, requiring ongoing intervention to maintain ecological balance. Tools designed for river maintenance often include specialized dredgers that prevent sediment buildup while enhancing water flow. The importance of river maintenance extends beyond the physical; it's crucial for sustaining ecosystems and complying with environmental regulations. Effective practices, such as controlled dredging, not only preserve riverine environments but also reduce erosion threats. An example of competent river management is the use of bank stabilization technologies to prevent erosion, demonstrating significant outcomes in preserving natural habitats.
Maintaining a balance between effective weed control and preserving aquatic ecosystems is crucial for sustainable water management. Overzealous weed removal can disrupt delicate aquatic ecosystems and reduce biodiversity. To minimize ecological disruption, methods such as hand-pulling, which offers long-term results, and selective cutting of native plants using tools like weed cutters, are advisable. These practices ensure that only invasive species are removed while preserving beneficial native vegetation. Experts like those at Waterfront Restoration suggest employing strategies that mitigate the ecological impact and adhere to sustainable management guidelines. An example of successful weed management can be seen in efforts to control invasive milfoil, which involves cutting before seed production and thorough equipment cleaning to prevent further spread. Sustainable practices ensure both water clarity and ecological balance, promoting overall health for aquatic ecosystems.
Water maintenance activities, such as dredging or aquatic weed harvesting, present potential pollution risks that need mitigating to preserve water quality. The main pollution sources include sediment disturbance, oil leaks from machinery, and improper waste disposal. Effective technologies and practices can help prevent contamination, such as using eco-friendly dredgers and ensuring proper maintenance of equipment to avoid leaks. Regulatory guidelines further emphasize minimizing environmental impacts, stressing the importance of adherence to cleanliness and safety protocols. Successful pollution prevention is exemplified by projects employing floating barriers during dredging to contain suspended particles and prevent them from spreading across water bodies. Such strategic measures, along with adherence to environmental regulations, play a pivotal role in maintaining clean and healthy water systems during maintenance operations, ultimately safeguarding aquatic and human health.
In marine environments, corrosion prevention is crucial for maintaining the longevity of equipment used in aquatic applications. The aggressive nature of saltwater significantly accelerates the corrosion process, which can lead to increased maintenance costs and a reduced lifespan for equipment. To combat these challenges, implementing best practices such as using corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel and titanium is vital. According to experts in marine maintenance, these materials offer superior resistance to the corrosive effects of saltwater, thereby extending the life of the equipment significantly. Additionally, regular application of marine-grade lubricants and protective coatings can further shield equipment from harmful environmental factors.
The statistical impact of corrosion is evidenced by the fact that it contributes to a significant portion of maintenance expenses in marine industries. Studies indicate that corrosion can increase maintenance costs by up to 30% if not adequately addressed. Successful examples from organizations such as the U.S. Navy, which applies stringent corrosion prevention programs, highlight how these efforts lead to substantial savings and enhanced equipment reliability. By adopting these proven methods, marine operators can protect their investments and ensure operational efficiency.
Seasonal maintenance is essential for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of dredging and harvesting equipment used in water bodies. Different seasons bring diverse environmental challenges that can impact equipment performance. For instance, winter months can lead to freezing conditions that may damage machinery if not properly winterized, while spring and summer bring increased usage and potential wear and tear.
A comprehensive checklist for seasonal equipment care should include inspecting and replacing worn parts, applying lubricants to moving components, and ensuring all hydraulic and electrical systems are functioning correctly. Cases such as those of large-scale dredging operations on the Mississippi River have demonstrated the benefits of thorough seasonal maintenance, resulting in extended equipment life and reduced unexpected breakdowns.
For operators, enhancing safety during maintenance tasks is paramount. Guidelines include using personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and eye protection, conducting risk assessments before any major maintenance activity, and ensuring proper training for maintenance personnel. By following these practices, operators can not only maintain their equipment more effectively but also ensure a safe working environment during maintenance operations.