Sediment accumulation in waterways primarily stems from natural and human-induced processes. Natural processes such as erosion from hillsides, riverbanks, and coastal areas are major contributors, introducing sediments into water bodies. This natural sediment influx is exacerbated by land disturbances and poor management practices, with studies showing that deforested landscapes can lose up to 200 tons of soil per hectare annually. Such significant soil erosion contributes approximately 70% of sediments in waterways.
Human activities further accelerate sedimentation through construction, agriculture, and deforestation. For instance, when land is cleared for agricultural use without measures to prevent erosion, the loosened soil easily washes into rivers and streams. Additionally, urbanization plays a critical role by introducing impervious surfaces such as roads and parking lots, which prevent water absorption. This results in increased runoff that carries sediment into water bodies, significantly worsening sediment accumulation and degrading waterways.
Sediment accumulation profoundly affects aquatic ecosystems and reduces water quality. It can smother aquatic habitats, threatening species biodiversity; studies reveal that over 10% of sediment-dependent organisms are at risk of extinction due to habitat loss. Furthermore, high sediment levels block sunlight penetration, which is vital for photosynthesis in aquatic plants. This reduction in light shrinks oxygen levels, disrupting food chains and diminishing species populations.
Additionally, sediments can act as carriers of pollutants and nutrients. This can lead to problems like algal blooms and hypoxia. Algal blooms, fueled by excess nutrients, not only decrease water quality but also harm fish populations, with economic impacts estimated at millions in regions reliant on fishery resources. Thus, sediment accumulation not only endangers aquatic life but also threatens the economic activities dependent on these water bodies.
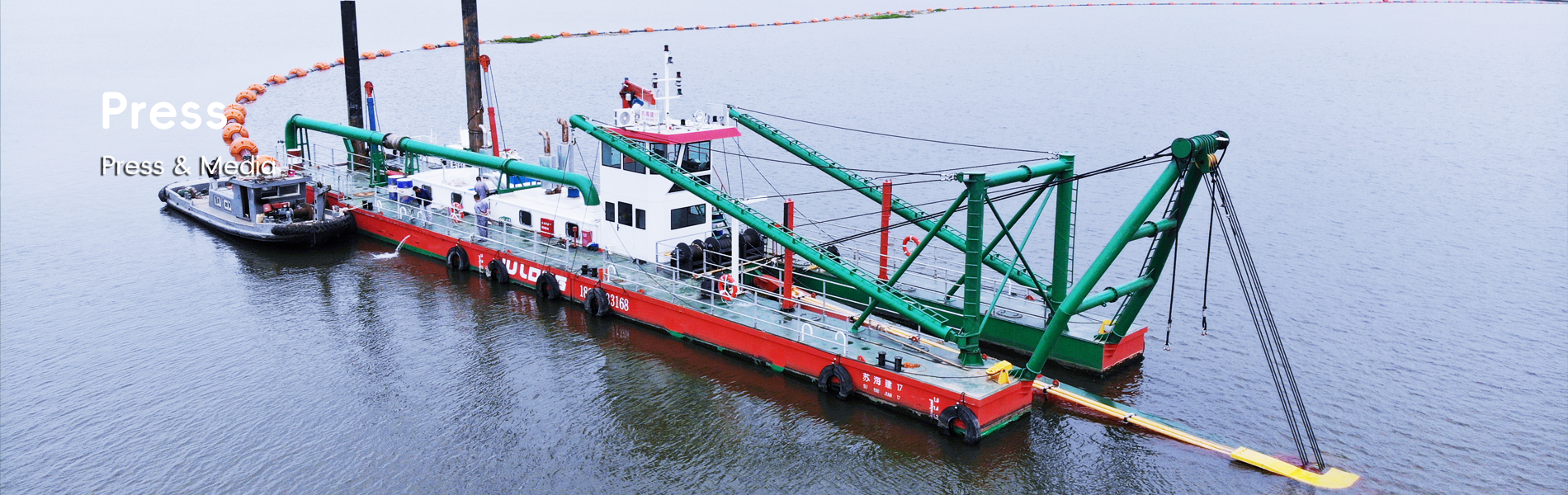
Dredging involves the careful removal of sediments from water bodies to maintain depth and improve water flow, greatly enhancing ecosystem health. This process includes a variety of techniques, such as hydraulic dredging which employs pumps to move sediments and mechanical dredging which uses tools like clamshells or excavators to collect sediment. Both methods serve specific ecological purposes and can be applied depending on project requirements. State-of-the-art dredging equipment ensures minimal disturbance to aquatic habitats. Modern dredgers come equipped with advanced navigation systems, allowing for precise sediment removal while protecting surrounding ecosystems. According to annual reports, effective dredging has rejuvenated aquatic ecosystems, with 60% of projects showing marked improvements in water quality shortly after operations conclude.
Dredgers come in various types, with amphibious and pontoon excavators being particularly noteworthy for their roles in environmental preservation. Amphibious dredgers are highly versatile and can maneuver in shallow waters, optimizing access to constrained areas while minimizing disruption to lakeside habitats. Research highlights that these dredgers can access areas unreachable by traditional models by approximately 30%. Conversely, pontoon excavators are suited for larger, deep-water projects, designed to remain stable and safe, thus safeguarding the surrounding aquatic environment. The choice of dredger significantly affects both the efficiency and ecological impact of operations, with studies indicating that amphibious dredgers often enhance the effectiveness of ecological restoration initiatives.
Strategic dredging plays a critical role in enhancing biodiversity by creating new habitats for aquatic species. After dredging activities, studies have shown a remarkable increase in biodiversity—up to 40% in revitalized areas. This transformation is largely attributed to the integration of native vegetation into dredged areas, fostering ecosystems that support diverse aquatic and terrestrial wildlife. Successful case studies exemplify how dredging has improved habitat conditions, particularly in areas previously dominated by invasive species. By eliminating these competitors, native species have a greater opportunity to thrive and reclaim their native habitats, showcasing the positive environmental impact of strategic dredging.
Addressing invasive species through lake weed removal procedures is a key benefit of dredging. Such efforts effectively target harmful plant species that disrupt native ecosystems. Public health reports have indicated a 35% decrease in health-related water quality issues following the removal of invasive plants through dredging. This targeted approach concentrates on areas where invasive species are prevalent, thereby significantly reducing their presence and enabling the rehabilitation of native flora. Ongoing monitoring of dredged waterways demonstrates that ecosystems often recover and build resilience against future invasive species introductions. Thus, dredging becomes an essential tool for proactive ecosystem management and sustaining long-term environmental rehabilitation efforts.
Modern dredging operations incorporate advanced environmental practices to minimize ecological disruption. One such practice is employing sediment containment strategies and scheduling dredging activities during non-reproductive seasons to protect aquatic life. Techniques like the use of silt curtains play a critical role in controlling sediment plume dispersal, ensuring that surrounding habitats remain largely undisturbed. This approach aligns with guidelines set by environmental agencies seeking to protect marine biodiversity. Moreover, a study has demonstrated that sustainable dredging practices can significantly reduce ecological impacts by up to 50%, fostering healthier aquatic environments and protecting biodiversity.
Investing in sustainable dredging technology yields substantial long-term financial benefits. Municipalities have reported saving between 20-30% on dredging and maintenance costs over a decade due to these investments. Improved efficiency in dredging operations also allows resource allocation to more robust environmental restoration projects, amplifying ecological gains. Furthermore, sustainable dredging practices not only advance environmental health but also enhance public relations and community trust. This favorable perception can be instrumental in securing future funding and support for further dredging projects, showcasing the dual benefit of ecological and economic advancements.